Physics is the branch of science that studies matter, energy, and their interactions. It governs everything from the tiniest particles to the largest galaxies. While some laws of physics seem straightforward, others are downright strange. Here are 18 weird laws of physics that will make you see the universe in a whole new light.
Quantum Entanglement

Quantum entanglement is a phenomenon where particles become linked and instantly affect each other, no matter how far apart they are. This means that a change in one particle instantly causes a change in another, even if they are light-years apart.
The Uncertainty Principle

The Uncertainty Principle, formulated by Werner Heisenberg, states that you cannot precisely know both the position and momentum of a particle at the same time. The more accurately you know one, the less accurately you can know the other.
Time Dilation

According to Einstein’s theory of relativity, time moves slower for objects in motion compared to those at rest. This means that astronauts traveling at high speeds age more slowly than people on Earth.
Wave-Particle Duality
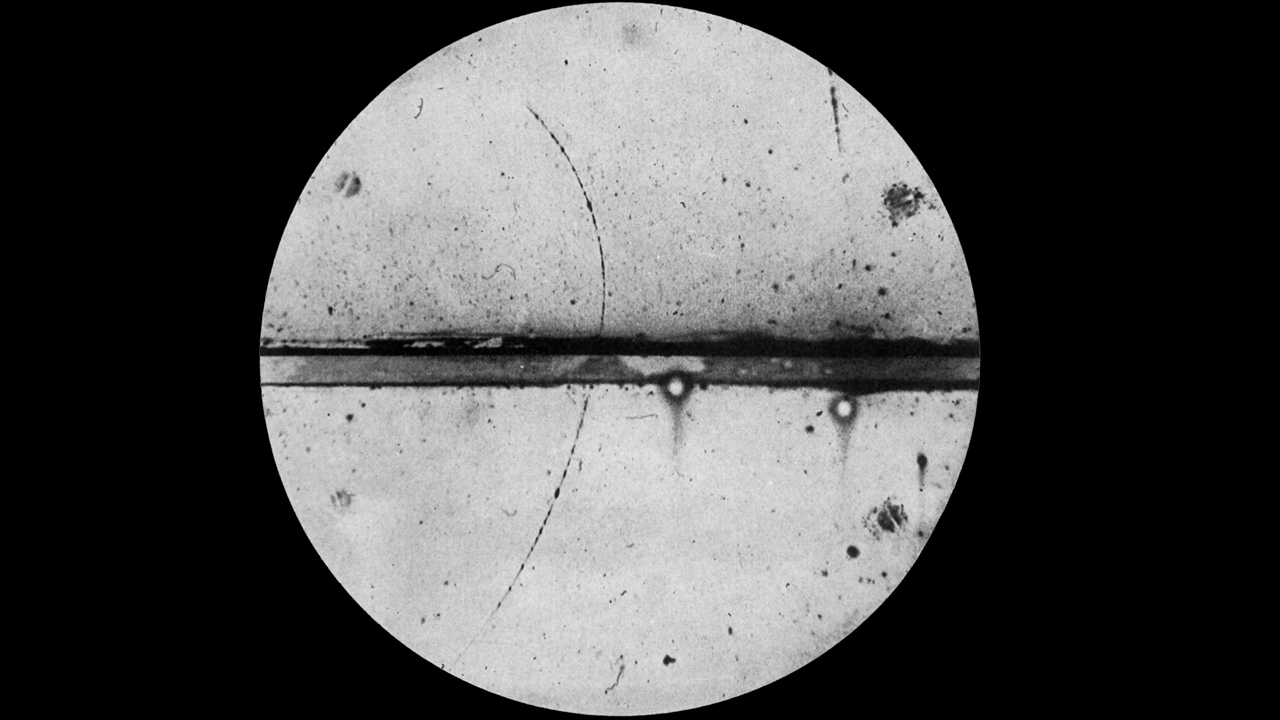
Wave-particle duality is the concept that particles like electrons and photons exhibit both wave-like and particle-like properties. This means that sometimes they behave like particles and other times like waves.
Schrödinger’s Cat

Schrödinger’s Cat is a thought experiment that illustrates the weirdness of quantum mechanics. It suggests that a cat in a sealed box can be both alive and dead until someone opens the box and observes it.
Black Hole Information Paradox

The black hole information paradox is the puzzling idea that information about matter falling into a black hole could be lost forever, which contradicts the laws of quantum mechanics that state information cannot be destroyed.
Gravitational Waves

Gravitational waves are ripples in spacetime caused by massive objects like merging black holes. These waves travel at the speed of light and can pass through anything, stretching and squeezing space as they go.
Dark Matter

Dark matter is a mysterious substance that makes up about 27% of the universe. It does not emit, absorb, or reflect light, making it invisible and detectable only through its gravitational effects on visible matter.
Dark Energy

Dark energy is an unknown force that is causing the universe to expand at an accelerating rate. It makes up about 68% of the universe and counteracts the pull of gravity.
The Pauli Exclusion Principle

The Pauli Exclusion Principle states that no two fermions (particles like electrons) can occupy the same quantum state simultaneously. This principle explains the structure of the periodic table and the stability of matter.
Hawking Radiation

Hawking radiation is a theoretical prediction by Stephen Hawking that black holes can emit radiation due to quantum effects near the event horizon. This means that black holes can slowly lose mass and eventually evaporate.
Quantum Tunneling

Quantum tunneling is the phenomenon where particles can pass through barriers that they shouldn’t be able to, according to classical physics. This is possible because of the wave-like nature of particles in quantum mechanics.
The Casimir Effect
The Casimir effect is a physical force arising from the vacuum energy between two uncharged, parallel plates placed very close to each other. This force is due to the quantum fluctuations of the vacuum.
Tachyons

Tachyons are hypothetical particles that travel faster than light. If they exist, they would violate Einstein’s theory of relativity, which states that nothing can travel faster than light.
The Double-Slit Experiment
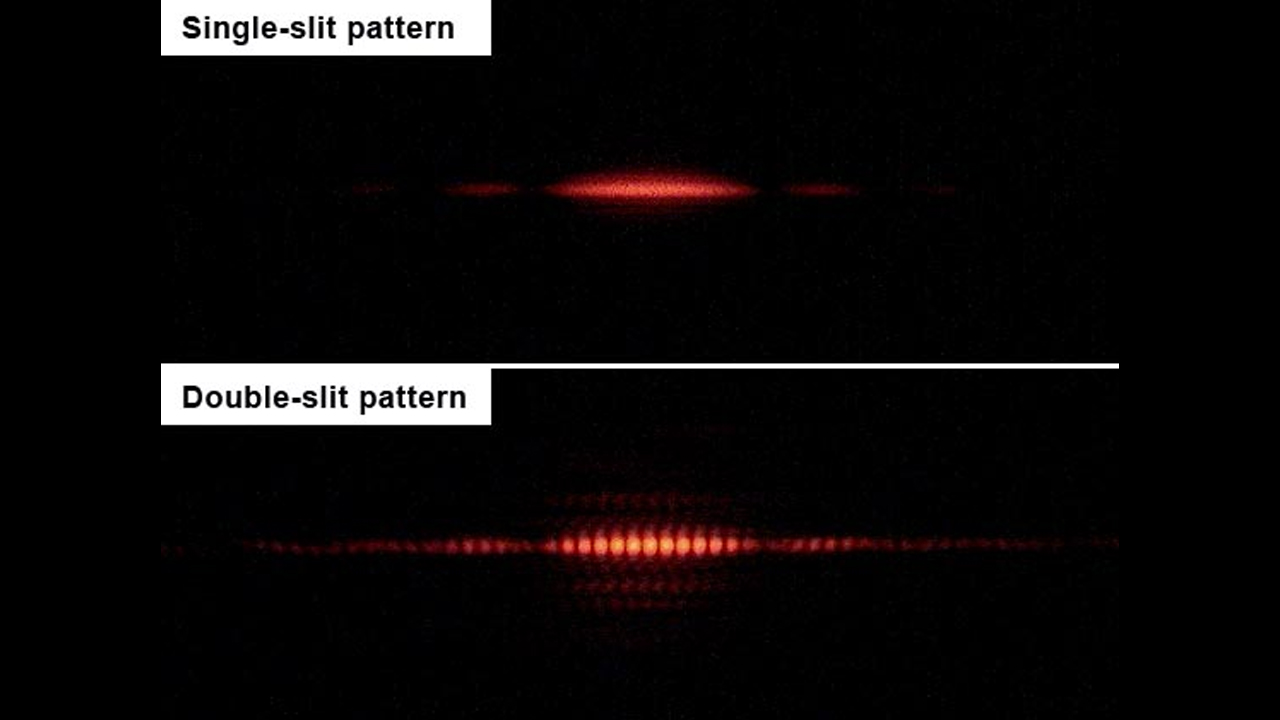
The double-slit experiment demonstrates that light and matter can display characteristics of both waves and particles. When particles pass through two slits, they create an interference pattern, revealing their wave-like behavior.
The EPR Paradox

The EPR paradox, named after Einstein, Podolsky, and Rosen, challenges the completeness of quantum mechanics. It suggests that particles can instantly affect each other, implying that information can travel faster than light.
Quantum Foam

Quantum foam is a concept that describes the fluctuating, foamy structure of spacetime on the smallest scales. It suggests that at very small distances, spacetime is not smooth but constantly changing due to quantum effects.
The Multiverse Theory

The multiverse theory proposes that our universe is just one of many universes that exist. These parallel universes could have different physical laws and constants, making them vastly different from our own.
Ellen has been obsessed with logic puzzles, jigsaws, and cryptograms since she was a kid. After learning she was taught how to play chess wrong by a family friend (so they could win), she joined her school chess club and the rest is history.

