Science is a never-ending source of wonder, constantly revealing truths about our world that challenge our understanding and stretch our imagination. From the tiniest particles to the vastness of the cosmos, scientific discoveries often border on the unbelievable. Yet, these mind-bending facts are grounded in rigorous research and observation. They remind us that reality is often stranger than fiction and that the universe is far more extraordinary than we might have ever dreamed. In this list, we’ll explore 24 scientific facts that might seem too wild to be true, but are actually well-established in the scientific community. Prepare to have your mind blown by the astonishing realities of our world!
Your Body Contains Stardust

Every atom in your body, except for hydrogen, was created inside a star. When massive stars explode as supernovae, they scatter these elements across space. Over billions of years, these star-forged atoms have been incorporated into everything on Earth, including you. This means you’re literally made of stardust. Remarkably, some of the heaviest elements in your body, like gold and platinum, were likely created during the collision of neutron stars.
Water Can Boil and Freeze at the Same Time

At a specific temperature and pressure, known as the triple point, water can exist as a solid, liquid, and gas simultaneously. This occurs at 0.01°C and 0.006 atm pressure. At this precise point, you could witness water boiling and freezing at the same time. This phenomenon is used in some scientific instruments for calibration purposes.
Time Passes Faster at the Top of Buildings
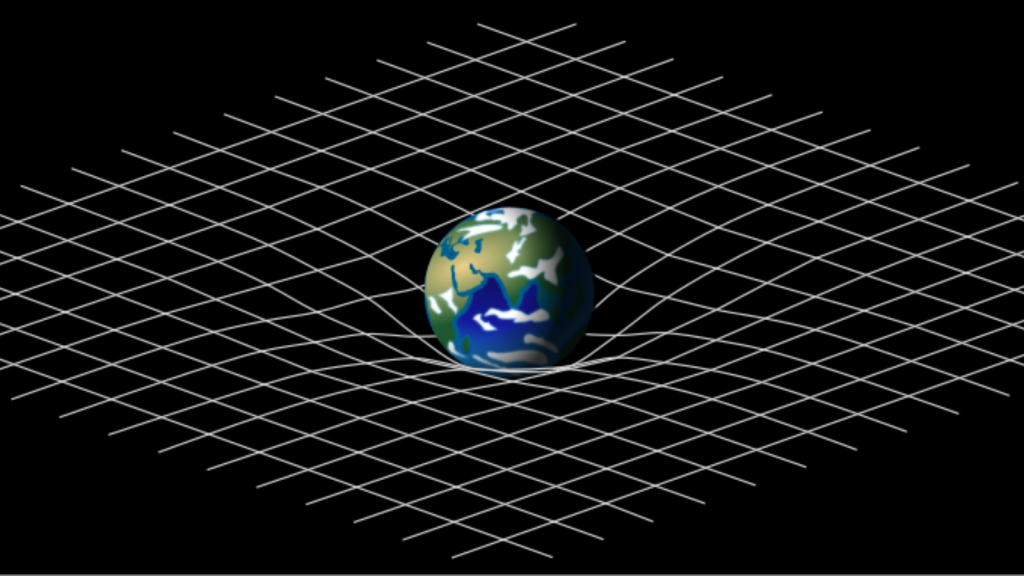
According to Einstein’s theory of relativity, time moves slower in stronger gravitational fields. This means time actually passes slightly faster at the top of a building compared to the bottom. While the difference is tiny for buildings, atomic clocks can measure this effect. GPS satellites have to account for this time difference to maintain accuracy.
Quantum Particles Can Be in Two Places at Once
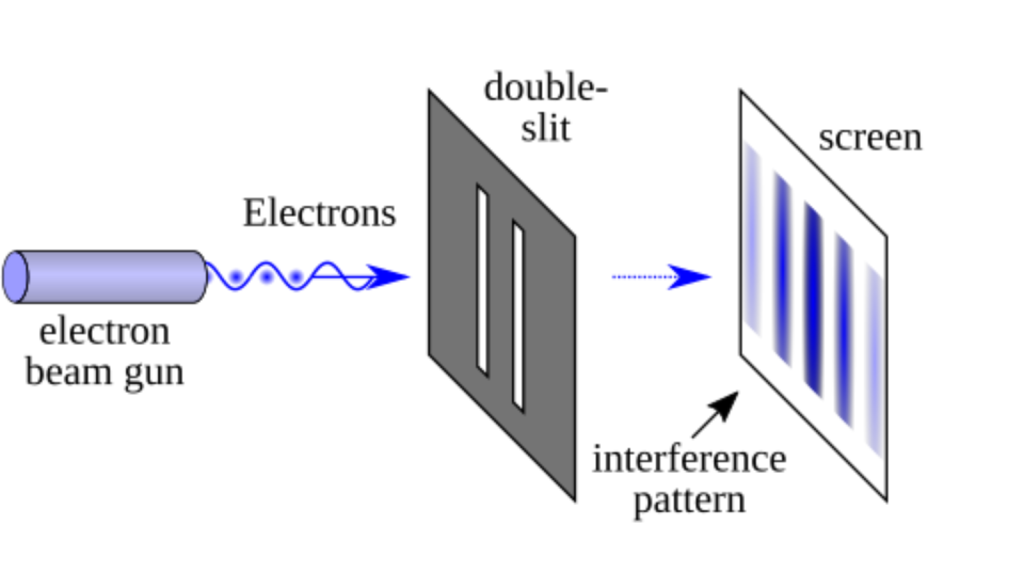
In the quantum world, particles can exist in multiple states simultaneously, a phenomenon called superposition. This bizarre behaviour is the basis for quantum computing. It’s only when we observe or measure a particle that it “decides” which state to be in. This principle is demonstrated in the famous “double-slit experiment,” which shows particles behaving as both particles and waves.
A Teaspoonful of Neutron Star Would Weigh Billions of Tonnes

Neutron stars are incredibly dense. A sugar cube-sized piece of neutron star material would weigh as much as all of humanity. Their gravity is so intense that a one-millimetre fall on a neutron star’s surface would release enough energy to vaporise you. Neutron stars are so dense because they’re essentially gigantic atomic nuclei, with electrons and protons crushed together to form neutrons.
Bananas Are Slightly Radioactive

Bananas contain potassium-40, a naturally occurring radioactive isotope. Don’t worry, though – you’d need to eat about 10 million bananas in one sitting to die of radiation poisoning. The radiation from bananas is so low that they’re often used to illustrate the concept of everyday, harmless radiation exposure. This radiation is actually detectable by sensitive equipment used to scan for nuclear materials at ports.
Some Animals Can Regrow Their Heads

Several species of sea slugs can detach their heads and regrow an entire new body. This process, called autotomy, allows them to shed a parasite-infested body and start fresh. The head can continue to eat and move around while it regenerates its body over a few weeks. This remarkable ability is due to stem cells clustered near their heads, which can develop into any type of cell needed for regeneration.
The Earth’s Core Is as Hot as the Surface of the Sun
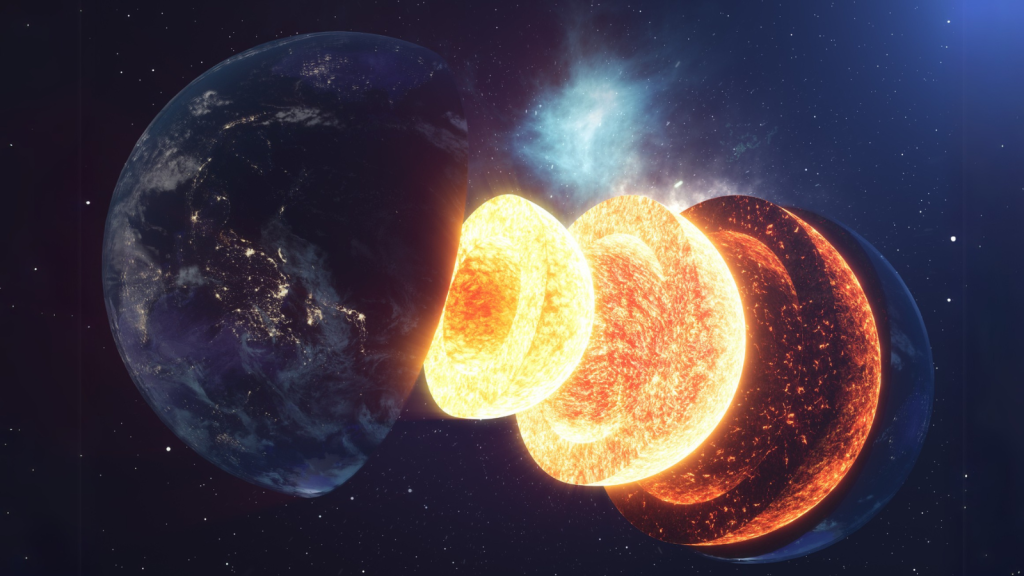

The inner core of our planet reaches temperatures of about 5,400°C (9,800°F), which is roughly the same as the surface of the Sun. This extreme heat is partly leftover from the Earth’s formation and partly generated by the decay of radioactive elements. Despite this intense heat, the inner core remains solid due to the enormous pressure exerted by the layers above it.
A Day on Venus Is Longer Than Its Year
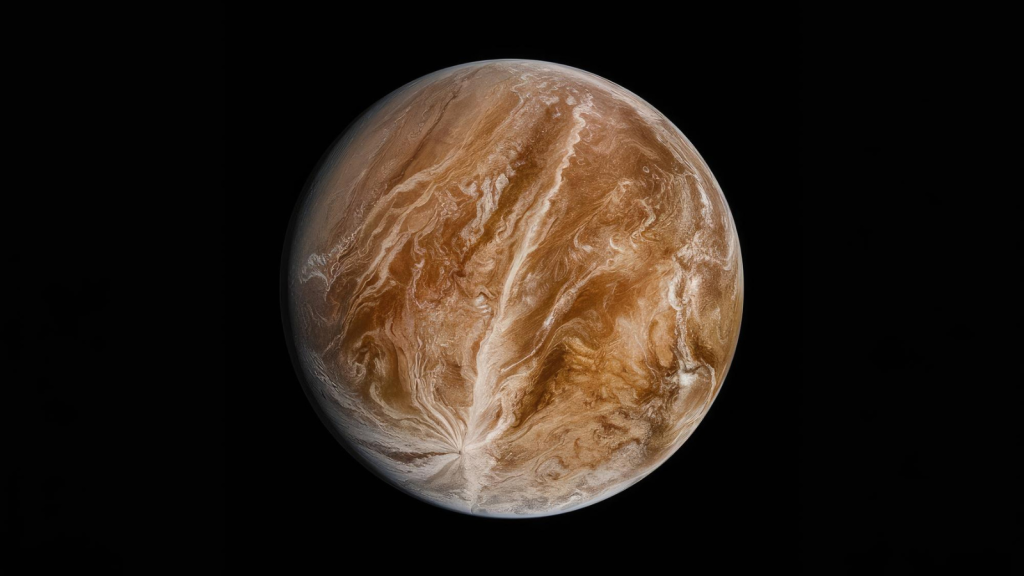

Venus rotates on its axis so slowly that it takes longer to complete one rotation (a day) than it does to complete one orbit around the Sun (a year). A day on Venus lasts about 243 Earth days, while its year is only 225 Earth days. Even more peculiarly, Venus rotates in the opposite direction to most planets, a phenomenon known as retrograde rotation.
Tardigrades Can Survive in Space
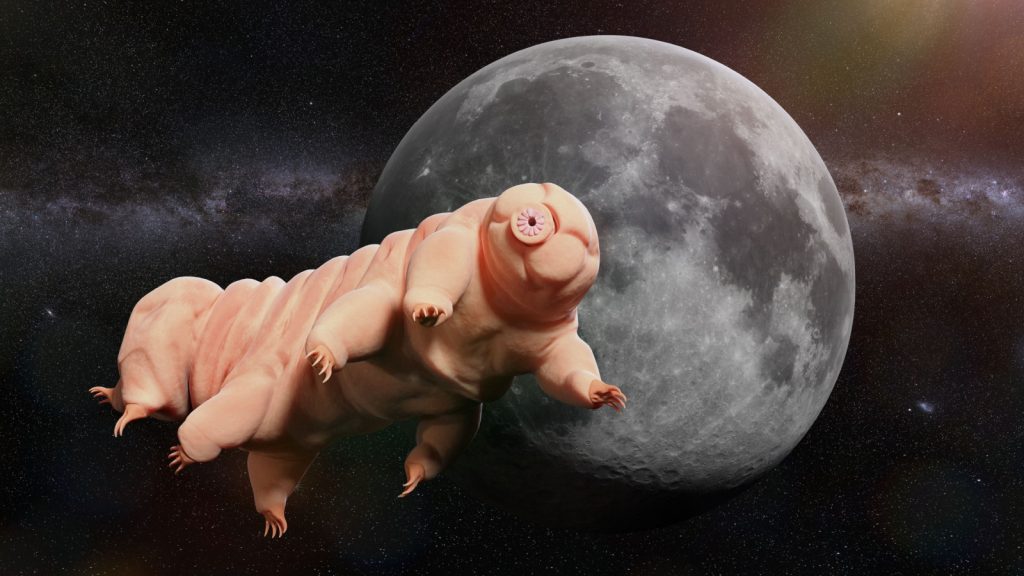

These microscopic creatures, also known as water bears, can survive extreme conditions that would kill most other life forms. They’ve been shown to survive the vacuum of space, extreme temperatures, high pressures, and even radiation levels far beyond what humans can tolerate. Tardigrades achieve this remarkable feat by entering a state called cryptobiosis, where they expel almost all water from their bodies and drastically slow their metabolism.
There Are More Trees on Earth Than Stars in the Milky Way

Recent estimates suggest there are about 3 trillion trees on Earth. In comparison, astronomers estimate there are between 100-400 billion stars in our galaxy. This means there are likely at least 7 times more trees on Earth than stars in the Milky Way. However, it’s worth noting that humans have reduced the number of trees on Earth by about 46% since the start of human civilization.
The Human Brain Uses About as Much Power as a Light Bulb

Your brain consumes about 20 watts of power, which is roughly the same as a low-energy light bulb. Despite using only 2% of your body’s weight, it uses about 20% of your body’s total energy. This energy powers the billions of neurons that make thinking possible. Interestingly, this energy consumption remains fairly constant whether you’re deep in thought or daydreaming.
Some Metals Can Explode If You Put Them in Water
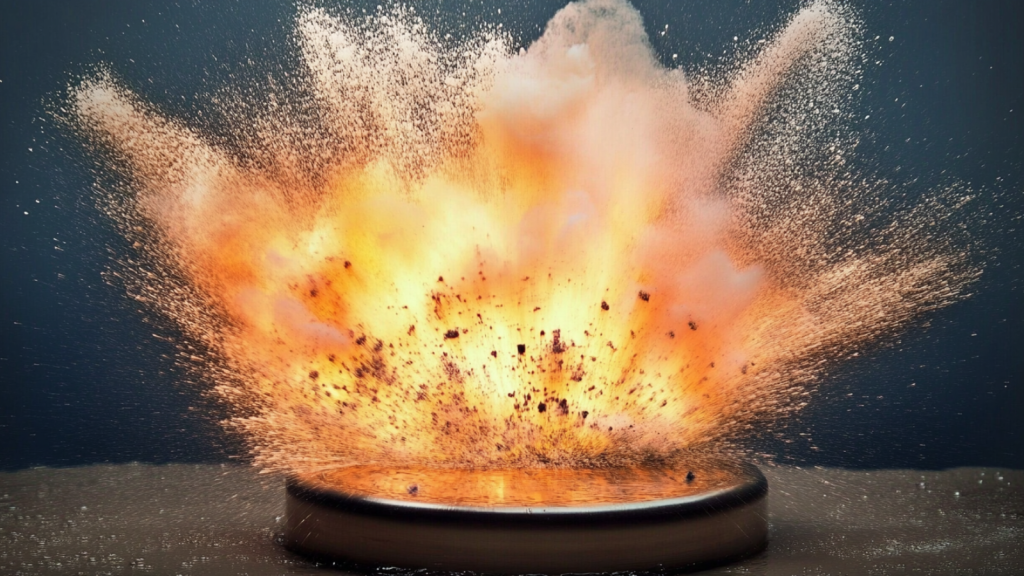

Certain alkali metals, like sodium and potassium, react violently when exposed to water. The reaction produces hydrogen gas and enough heat to cause an explosion. This is why these metals must be stored in oil to prevent contact with moisture in the air. The reaction becomes more violent as you move down the periodic table, with cesium and rubidium reacting explosively even with ice.
A Bucket of Earth Contains More Organisms Than There Are People on the Planet

A single handful of soil contains billions of microorganisms, more than the number of humans on Earth. These include bacteria, fungi, protozoa, and nematodes. This hidden ecosystem plays a crucial role in nutrient cycling and soil health. In fact, a single gram of soil can contain up to one billion bacterial cells from thousands of different species.
The Longest-Living Vertebrate Could Be Over 500 Years Old
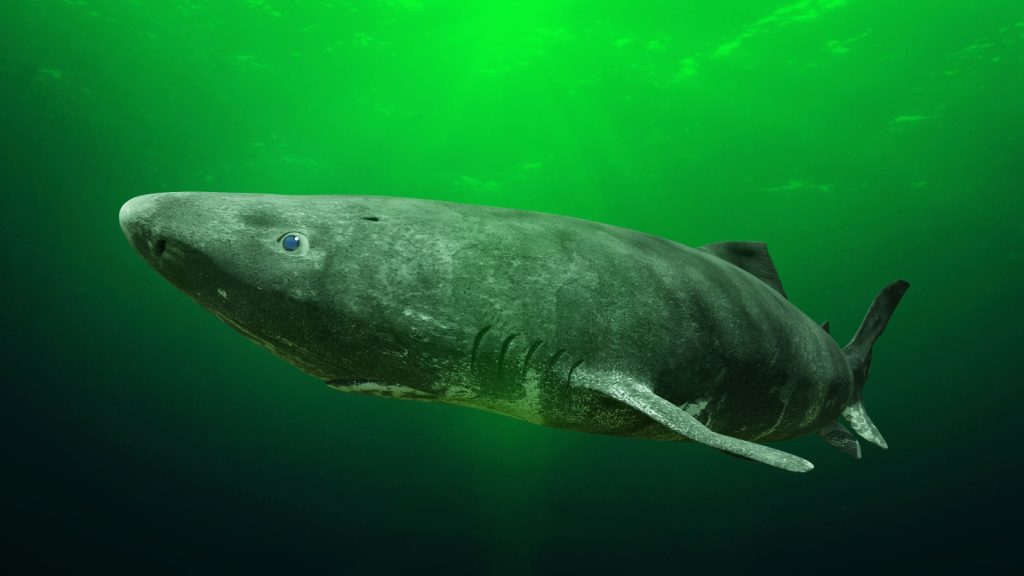

Greenland sharks are believed to be the longest-living vertebrates on Earth. Scientists estimate that these sharks can live for over 500 years. They grow extremely slowly, reaching sexual maturity at around 150 years old. Researchers determined their age by radiocarbon dating the sharks’ eye lenses, which do not change over their lifetime.
There’s a Gas Cloud in Space Full of Alcohol
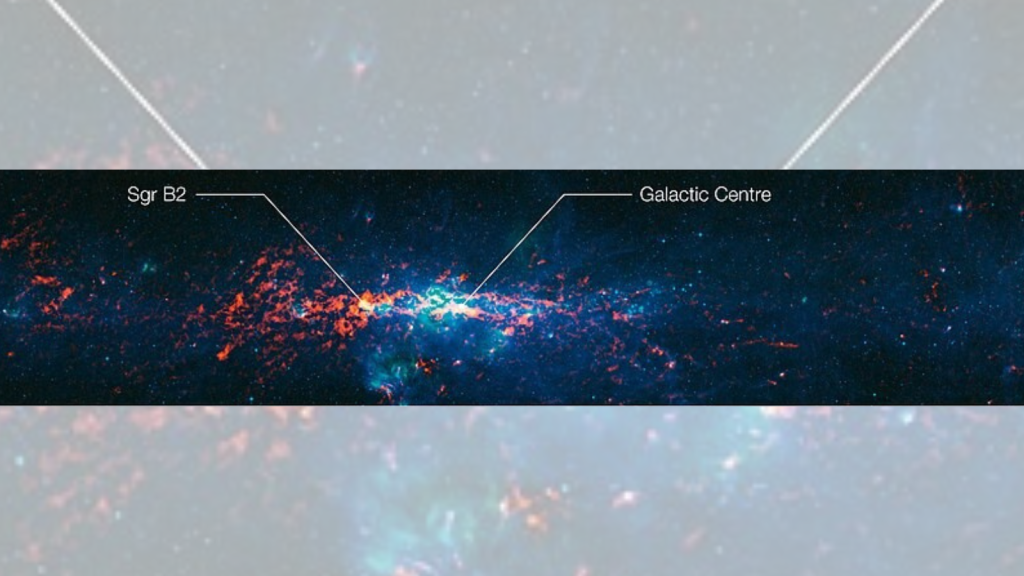
Sagittarius B2, a giant cloud of gas near the centre of our galaxy, contains enough ethyl alcohol to make 400 trillion trillion pints of beer. This cloud also contains other complex organic molecules, providing clues about how life might have originated. Astronomers have identified over 50 different molecules in this cloud, including ethylene glycol, the main ingredient in antifreeze.
Some Fungi Are Closer Relatives to Humans Than to Plants
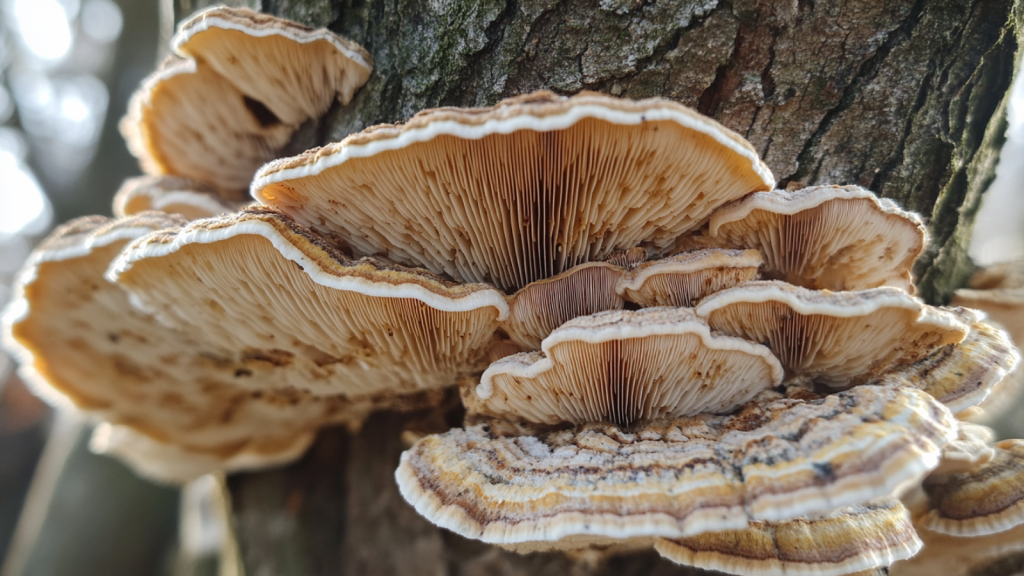

Genetically, fungi are more closely related to animals than to plants. Like animals, fungi cannot produce their own food and must absorb nutrients from their environment. This is why some scientists jokingly refer to humans as “advanced fungi”. This close relationship is also why many antibiotics that kill fungi can have side effects in humans.
A Tablespoon of a Neutron Star Would Weigh More Than Mount Everest
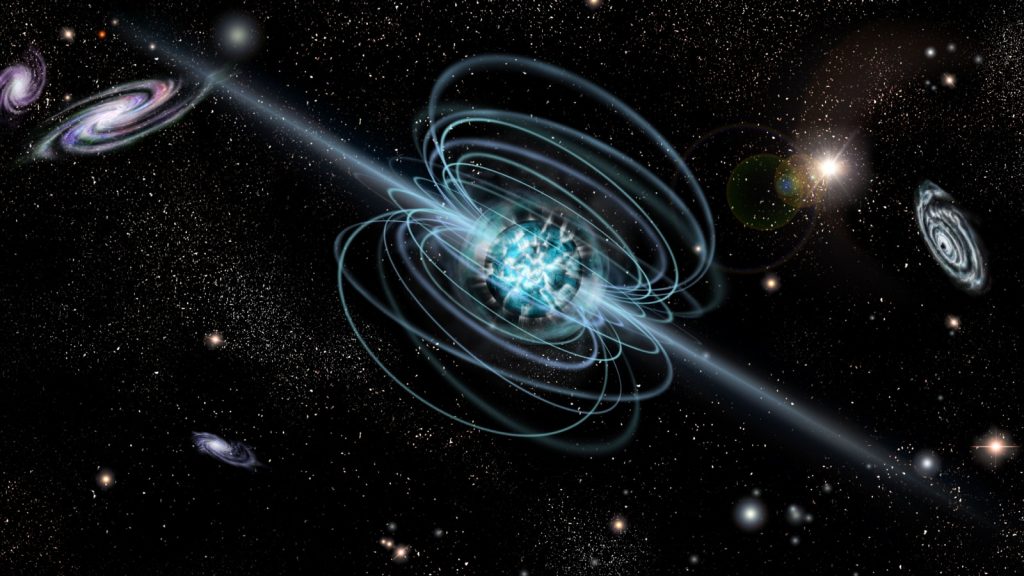

Neutron stars are so dense that a tablespoon of neutron star material would weigh about 10 billion tons. That’s more than the weight of Mount Everest. This incredible density results from the collapse of a massive star’s core during a supernova. The gravity on a neutron star is so intense that it can bend light, distorting our view of what’s behind it.
The Eiffel Tower Can Grow Up to 15 cm Taller in Summer
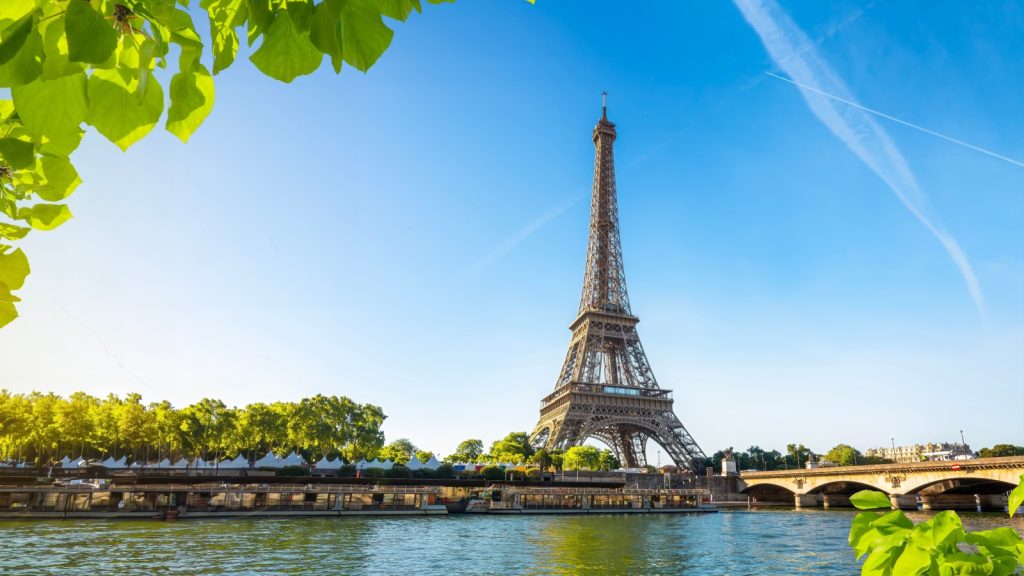

The iron structure of the Eiffel Tower expands when heated. On a hot summer day, thermal expansion can cause the tower to grow by up to 15 cm (6 inches). This expansion is carefully accounted for in the tower’s design to prevent structural issues. The tower also sways a few centimetres in strong winds.
Some Plants Can Count
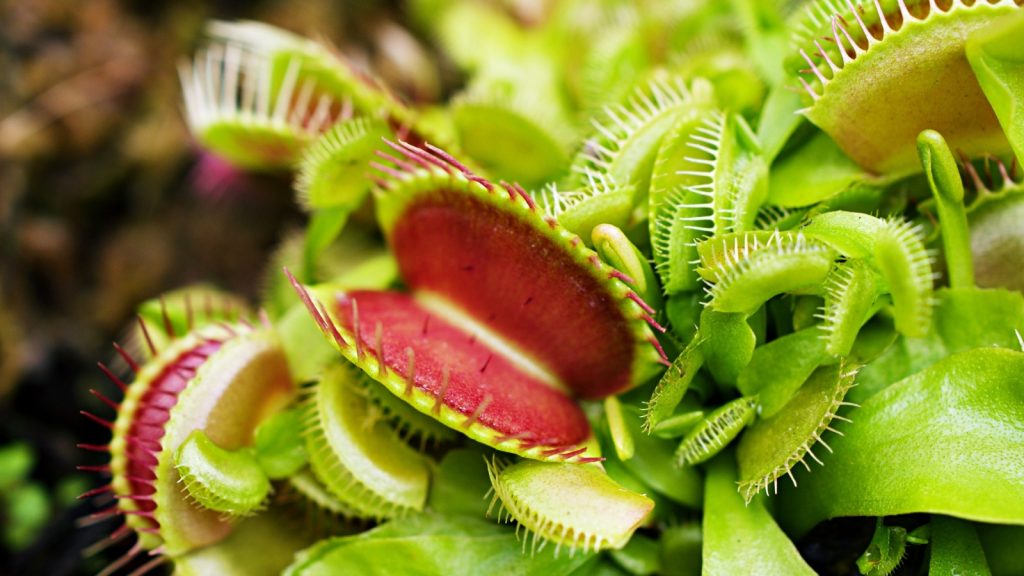

Venus flytraps can count the number of times their trigger hairs are touched. They typically wait for two touches within 20 seconds before snapping shut, which helps them avoid wasting energy on false alarms like raindrops. This counting ability is believed to be one of the most sophisticated behaviours observed in plants.
A Chicken Once Lived for 18 Months Without a Head

In 1945, a chicken named Mike survived for 18 months after his head was cut off. A small part of his brain stem remained intact, allowing basic functions to continue. He was fed with an eyedropper and became a touring sideshow attraction. Mike’s case is a remarkable example of the robustness of certain basic life functions in vertebrates.
Water Can Remain Liquid Below Freezing Point

Under certain conditions, water can be cooled below its freezing point without turning into ice, a phenomenon called supercooling. This can happen with very pure water that’s cooled slowly. A slight disturbance can cause this supercooled water to freeze instantly. This property is used in some instant ice packs and can occur naturally in clouds, leading to freezing rain.
There’s Enough DNA in the Human Body to Stretch from the Sun to Pluto and Back
If you uncoiled all the DNA in all the cells in your body and lined it up, it would stretch over 100 billion kilometres. That’s about 70 round trips between the Sun and Pluto. This vast amount of DNA is packed into the microscopic nucleus of each cell. Despite this length, the total weight of DNA in a human body is only about 0.2 grams.
Some Animals Can Reproduce Without Mating

Several species can reproduce through parthenogenesis, a form of asexual reproduction where an unfertilised egg develops into a new individual. This is common in some insects, reptiles, and fish. In rare cases, it’s even been observed in birds and sharks. While parthenogenesis produces genetically identical offspring, it allows species to reproduce when mates are scarce.
From Sunrise to Sunset: 19 Incredible Facts About the Sun That Will Light Up Your Universe

Our sun, an immense sphere of burning gas, and the centerpiece of our solar system, influences every aspect of life on Earth. But despite its everyday presence, many of us know little about its complexities and the pivotal role it plays.
Read More: From Sunrise to Sunset: 19 Incredible Facts About the Sun That Will Light Up Your Universe
What Science Fiction Gets Wrong About Mars and 23 Other Astonishing Planetary Facts

Our solar system is full of amazing and surprising facts that make each planet unique. From extreme temperatures to giant storms, there’s so much to learn about the planets that orbit our Sun. Here are 24 astonishing planetary facts that will leave you in awe.
Read More: What Science Fiction Gets Wrong About Mars and 23 Other Astonishing Planetary Facts
Katy Willis is a writer, master herbalist, master gardener, and certified canine nutritionist who has been writing since 2002. She’s finds joy in learning new and interesting things, and finds history, science, and nature endlessly fascinating.

