The human body holds many wonders and peculiarities that can surprise you. While many aspects of your body function smoothly and predictably, some lesser-known facts can be quite astonishing. These unusual facts may challenge what you thought you knew about your own biology.
What hidden secrets does your body hold? Exploring these curious and unexpected truths can deepen your appreciation for the complexities of human anatomy. Prepare to be amazed by the quirky and sometimes strange workings of your own body.
Humans Share 50% of Their DNA With Bananas

Did you know that you share 50% of your DNA with a banana? It sounds wild, but it’s true. Both humans and bananas have thousands of genes, and about half of them are similar. This doesn’t mean you are half banana, though. It just shows how genes can be similar in all living things.
Genes are like instructions that tell your body how to grow and function. Bananas and humans have many basic needs, like making cells and processing energy. So, it’s no surprise that we have some matching instructions. Think about it like two different recipes that share some of the same ingredients.
Scientists have studied DNA and found these similarities. It’s part of why we can learn about human genes by studying other organisms. Sharing DNA with bananas helps us understand our bodies better and can even help in research.
When people say we share 50% of our DNA with bananas, they mean that roughly half of our genes have a counterpart in bananas. This doesn’t mean half of your genetic material is from bananas, just that we have some genes in common.
So next time you eat a banana, remember you have more in common with it than you might think! This connection to bananas shows the incredible complexity and unity of life on Earth.
Your Nose Can Remember 50,000 Different Scents

You might think that your nose is just for breathing, but it’s capable of much more. One incredible thing it can do is remember around 50,000 different scents. This makes your sense of smell very powerful and versatile.
Think about different foods, flowers, and even the smell of rain. All these unique scents get stored in your brain because of your nose’s amazing ability. When you walk into your favorite bakery, it’s your nose that helps you recognize the smell of fresh bread.
Your nose has special cells called olfactory receptors that help detect these smells. These receptors send signals to your brain, which helps you identify and remember different scents. This means when you smell a rose, your nose and brain work together to recognize it again in the future.
Interestingly, researchers have found that the human nose can recognize more than just pleasant smells. It can detect danger, like smoke from a fire or spoiled food. This shows how helpful your nose can be in keeping you safe.
Your ability to recall these thousands of scents also plays a big role in forming memories. Scents can trigger powerful memories and emotions, often more vividly than sights or sounds. So next time you catch a whiff of something familiar, remember how amazing your nose really is.
The Human Brain Is 75% Water

Did you know your brain is mostly water? About 75% of it is made up of water. That’s a lot, considering how important your brain is.
The brain controls everything you do. It helps you think, feel, and move. With all that water, it’s like a sponge. This water helps your brain cells work well.
If you don’t drink enough water, your brain can’t work as well. You might feel tired, get headaches, or have trouble thinking clearly. Staying hydrated is really important for your brain.
Even though your brain is mostly water, it’s still very powerful. It uses about 20% of the oxygen and blood in your body. It’s amazing how something so wet can be so smart.
So, drink plenty of water every day. Your brain needs it to stay sharp and healthy. Remember, every sip you take helps your brain do its job better.
You Shed About 600,000 Particles of Skin Every Hour

Did you know that your body constantly sheds skin? Every hour, you lose around 600,000 particles of skin. This can add up over time. You shed roughly 1.5 pounds of skin each year.
This process is normal. Your body replaces old skin cells with new ones. Most of the dust in your home might actually be your dead skin. Scientists found that you might lose about 105 pounds of skin by age 70.
Your skin is the largest organ. It serves many roles like protecting you from germs and helping control body temperature. Despite its resilience, it renews itself frequently.
When you consider that your body naturally gets rid of so much skin, you realize how amazing your skin’s renewal process is. This shedding keeps your skin healthy and functioning properly. Taking care of your skin helps support this natural process. So, exfoliating and moisturizing can aid in removing dead skin and promoting new cell growth.
Think about this: every time you clean your room, some of that dust could be part of you. It’s a strange but fascinating part of being human.
Your Heart Beats Around 100,000 Times a Day

Your heart is an amazing organ. It beats around 100,000 times every day. That’s about 70 beats per minute.
Imagine how much work your heart does in one day. It pumps about 2,000 gallons of blood through your body. This blood travels around 12,000 miles daily—four times the distance across the United States.
The sound you hear when your heart beats is the sound of your heart valves opening and closing. These valves ensure blood flows in the right direction.
Throughout your life, your heart will beat about 2.5 billion times. That number shows just how strong and reliable this organ is.
Even though it weighs only about 11 ounces, your heart’s job is vital. Blood flowing through 60,000 miles of blood vessels reaches every part of your body. That’s enough to circle the Earth twice.
Knowing these facts makes you realize how important it is to take care of your heart. Simple things like eating well, staying active, and avoiding tobacco can keep your heart healthy. These small steps can help ensure your heart keeps beating reliably every day.
Humans Produce Enough Saliva to Fill Two Swimming Pools in a Lifetime
Did you know you produce a huge amount of saliva every day? An average person makes between 0.5 and 1.5 liters of saliva daily. Over a lifetime, this adds up to about 20,000 to 25,000 liters. That’s enough to fill two swimming pools!
Saliva isn’t just something that happens when you think of tasty food. It plays a big role in keeping your mouth healthy. It helps break down food, keeps your mouth moist, and protects your teeth from decay.
Every time you chew, talk, or even sleep, your body keeps producing saliva. This clear liquid contains important enzymes that start the digestion process right in your mouth. Without it, eating and speaking would feel very different.
This constant production means you are replacing saliva all the time. It’s like your own personal cleaning and maintenance crew working around the clock.
Your Bones Are 4 Times Stronger Than Concrete
Your bones are amazing. Pound for pound, they are four times stronger than concrete. This means if you had a piece of bone and a piece of concrete of the same size, the bone could handle four times more pressure before breaking.
This strength comes from the unique structure of bone. Bone has a strong outer layer called the cortex, which is dense and hard. Inside, there is a spongy layer called trabecular bone. This part has a mesh-like structure that makes it both strong and light.
Despite their strength, bones are still light. This balance allows you to move easily and quickly. While bone is very strong, it is also flexible. This flexibility helps it absorb impacts and prevents breakage. Stress and pressure can still cause fractures, but in many ways, bone’s flexibility saves you from more severe injuries.
Bone’s impressive strength means it can support heavy loads. For instance, the femur, your thigh bone, can support 30 times your body weight. It’s fascinating that our strongest materials in nature are inside us, allowing us to walk, run, and lift things with ease.
Even though bones are super strong, it’s still important to take care of them. Getting enough calcium and vitamin D helps keep your bones healthy. Regular exercise also strengthens your bones, making them even better at handling stress and pressure.
Imagine, every step you take, your bones are working hard to support you, doing a job that concrete could never do as well. This incredible strength and resilience are just one of the many amazing facts about your body.
The Acid in Your Stomach Is Strong Enough to Dissolve Razor Blades

Your stomach contains hydrochloric acid, which is very powerful. This acid has a pH level that ranges between 1 and 3. That’s strong enough to break down some metals, including razor blades. But don’t try swallowing one. It’s dangerous and not what your stomach is made for.
Scientists tested this by studying metal corrosion with stomach acid outside the body. They found that stomach acid can corrode razor blades fairly quickly. This study shows how strong the acid in your stomach really is. You can read more about this amazing fact here.
Even though your stomach acid can dissolve metals, it does not harm your stomach lining. Your body has special cells that protect your stomach from being digested by its own acid. It’s a good example of how amazing and complex your body is.
Remember, stomach acid is vital for digestion. It helps break down food, so your body can absorb nutrients. It’s fascinating to think that something so strong is also so essential for everyday life.
Humans Are the Only Species Known to Blush

When you feel embarrassed, your face turns red. This reaction is called blushing, and you are the only species that does it. Your blood vessels in the face get bigger, causing the skin to redden. This happens because nerves send signals to these vessels during stressful or embarrassing moments.
No other animal shows this unique reaction. Blushing serves as a non-verbal communication tool. It can show others that you feel ashamed, embarrassed, or even guilty. This can help smooth social interactions, showing you recognize a mistake or feel bad for an action.
Blushing might also build trust. When you blush, others may see you as more honest and trustworthy. They understand that you are experiencing a genuine emotion. This can help strengthen social bonds and create a better understanding between people.
Blushing remains a fascinating trait because it shows how complex human emotions are. It ties deeply to our social interactions and emotional responses.
The Average Person Has About 4 Pounds of Bacteria in Their Body
You might find it hard to believe, but your body hosts about 4 pounds of bacteria. These tiny organisms are everywhere inside you, especially in your gut. Although they are very small, they play a huge role in keeping you healthy.
Bacteria help with digestion, breaking down food so your body can absorb nutrients. Without them, you’d have trouble getting the vitamins and minerals you need. These microbes also help protect you from harmful bacteria and other germs.
In total, you have around 39 trillion bacteria living in your body. This sounds like a lot, and it is! These microbes actually outnumber your human cells. Scientists used to think the bacteria-to-human cell ratio was 10:1. Now, they believe it’s closer to 1.3:1.
The bacteria in your digestive system alone weigh about 2 to 6 pounds. Researchers with the NIH Human Microbiome Project have done extensive studies to figure out what types of bacteria live in a healthy person.
Even though it might seem strange, these bacteria are vital for your health. They play roles in digestion, mood regulation, and even your immune system. Next time you think about bacteria, remember how important they are for your well-being.
You Can’t Breathe and Swallow at the Same Time
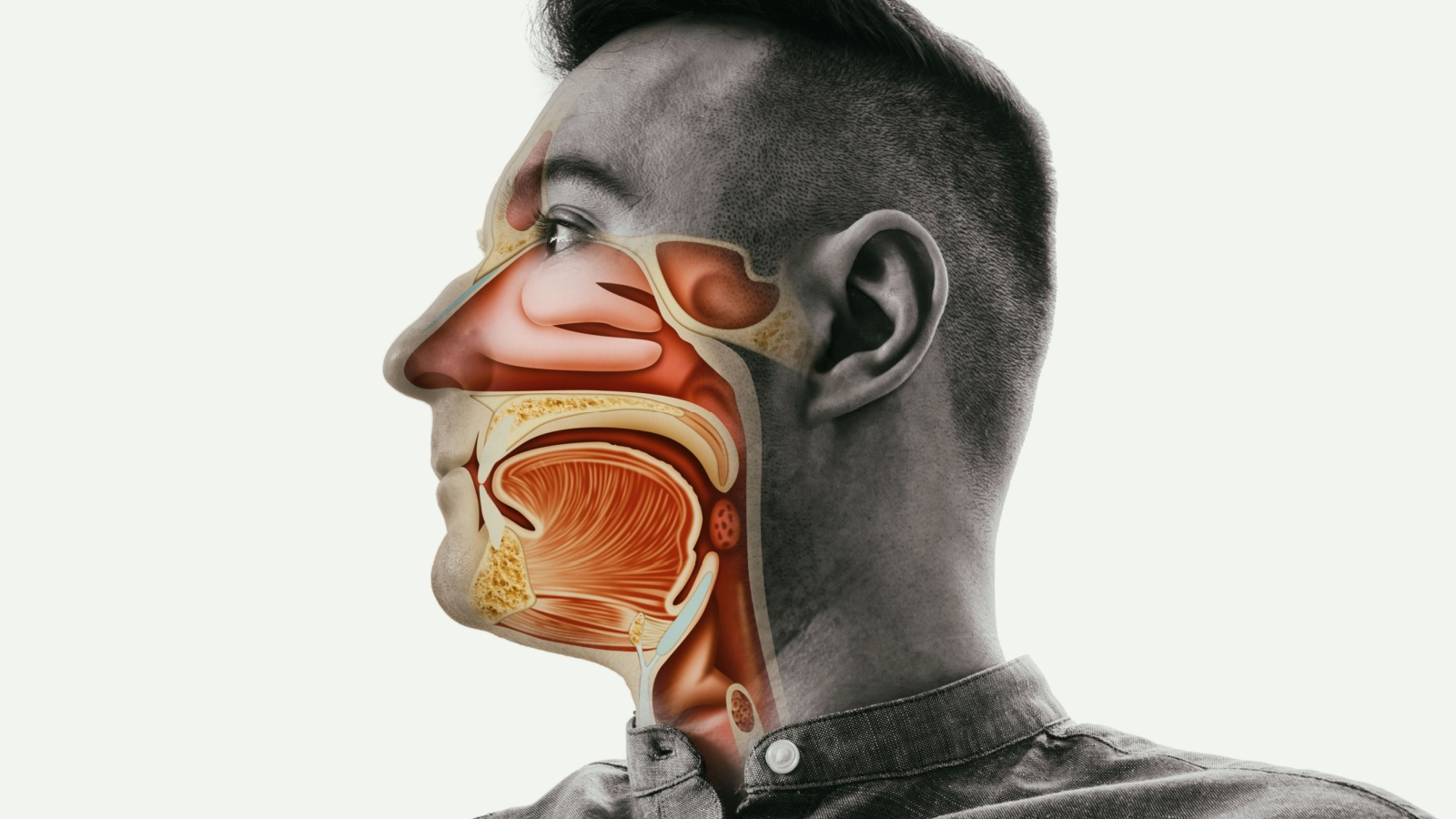
Your body is designed to either breathe or swallow, but not both at once. The reason lies in the structure of your throat. When you eat or drink, a small flap called the epiglottis moves to close off your windpipe. This prevents food or liquid from entering your lungs.
Breathing and swallowing use the same pathway at first but then diverge. When you swallow, the epiglottis covers your windpipe, directing food or drink down the esophagus. If you tried to breathe and swallow together, food could end up in your lungs, causing choking.
Tiny hairs called cilia line your throat and help keep you from choking. They move mucus and trapped particles away from your lungs. Your body naturally pauses breathing when you swallow to make sure you don’t inhale food or drink. This brief pause ensures safety, even if it means you can’t multitask these two actions.
So next time you enjoy a meal, remember the careful coordination happening in your throat. It’s a natural safeguard built to protect you from harm.
Your Hair Can Support the Weight of Two Elephants

You might find it hard to believe, but your hair is incredibly strong. Each strand of hair can support up to 3 ounces of weight. When you put all the hair on your head together, it adds up to something much more impressive.
Imagine this: the average human head has about 100,000 hair strands. All these strands combined can support up to 12 tons. That’s roughly the weight of two grown elephants. Think about the size and strength of an elephant for a moment. It’s almost impossible to imagine that your hair is that strong, but it truly is.
Hair is made of keratin, a protein that is also found in animal horns and hooves. This makes it both tough and flexible. When wet, hair can stretch up to 30% of its original length without breaking. This elasticity adds to its incredible strength.
Humans Are Born With Only Two Innate Fears: Falling and Loud Sounds

You might think that humans have a lot of fears from birth, but we actually only come with two built-in fears: falling and loud sounds. Scientists have found that these are the only fears all babies show without having to learn them.
Imagine a baby on the edge of a surface that looks like a drop-off. The baby will stop and hesitate, indicating a fear of falling. This fear helps protect us from dangerous heights even before we understand the concept of danger.
Loud noises also startle babies easily. Think about the sudden bang of a door slamming or a clap of thunder. This reaction serves as a defense mechanism. The quick response can help prepare the body for fight or flight, which increases the chances of survival in dangerous situations.
Studies show that as early as six months, infants respond to both these fears. For example, research from the 1960s revealed that babies aged 6 to 14 months would hesitate to crawl onto a glass floor that looked like a drop-off. This shows a natural fear of falling.
Similarly, when exposed to loud sounds, every baby showed a startle response. This quick reaction to sound helps prepare them for potential threats. Even though we develop many more fears as we grow, falling and loud sounds are the only two we’re born with. These fears keep us safe from the moment we enter the world.
Your Skin Renews Itself Every 28 Days
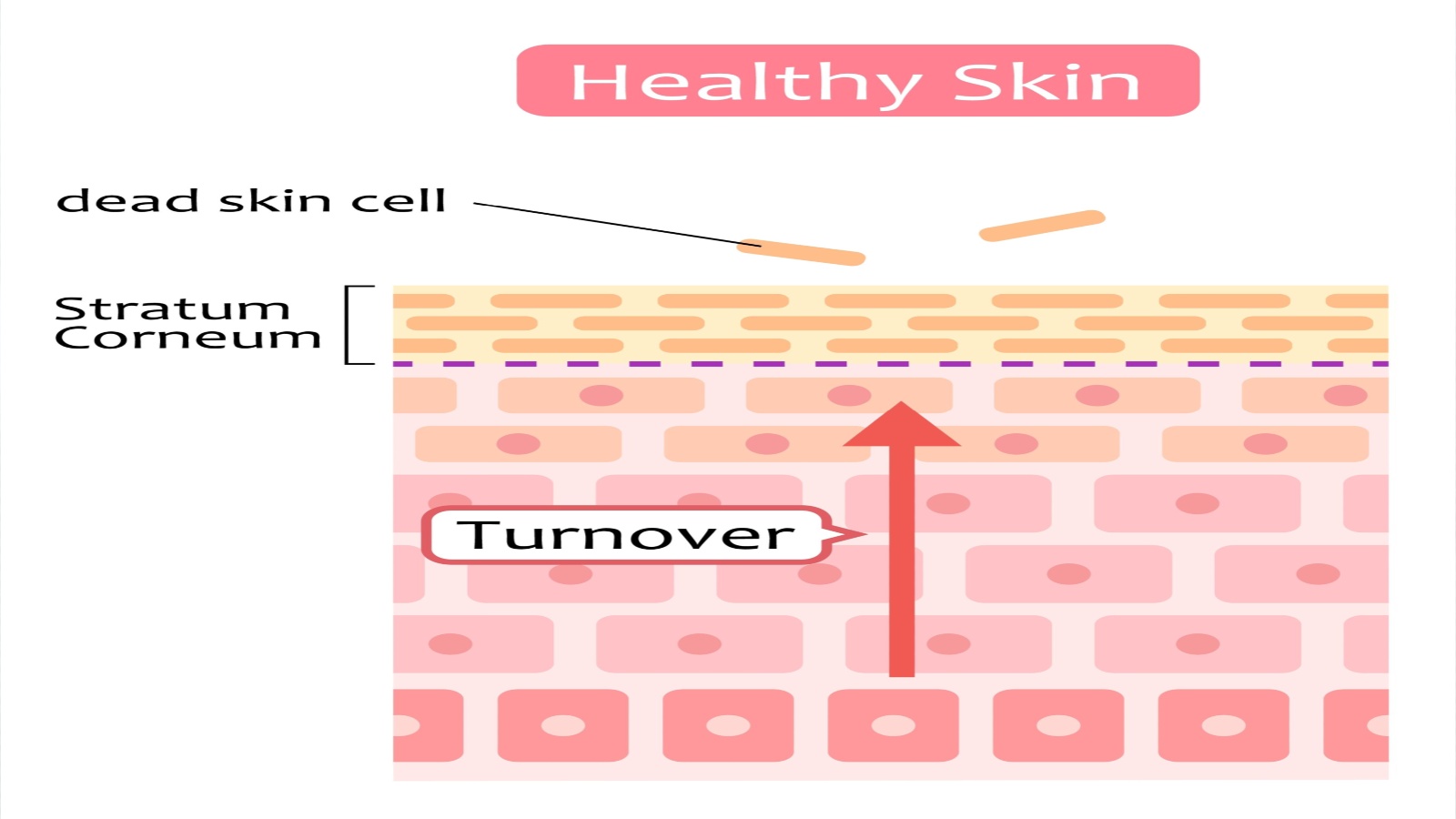
Your skin constantly works to keep you protected. Every 28 days, it goes through a complete renewal process. This means that, within a month, you have an entirely new layer of skin.
The process starts in the deeper layers of your skin. New cells form and push older cells toward the surface. As these cells move up, they eventually become part of the outermost layer, the epidermis.
Once they reach the surface, the dead cells naturally flake off. You might not even notice this happening, but it’s a continuous cycle. During this time, your skin sheds about 30,000 to 40,000 cells every minute. That’s almost 9 pounds of cells each year.
This renewal process plays a crucial role in keeping your skin healthy and fresh. It helps repair any damage, such as cuts or scrapes, and removes potentially harmful pathogens.
Maintaining this cycle depends on a healthy lifestyle. Eating a balanced diet, drinking plenty of water, and getting enough sleep all support your skin’s ability to renew efficiently. If you take care of your skin, it will continue to renew itself effectively every 28 days.
A Single Human Blood Cell Takes 60 Seconds to Make a Complete Circuit of the Body
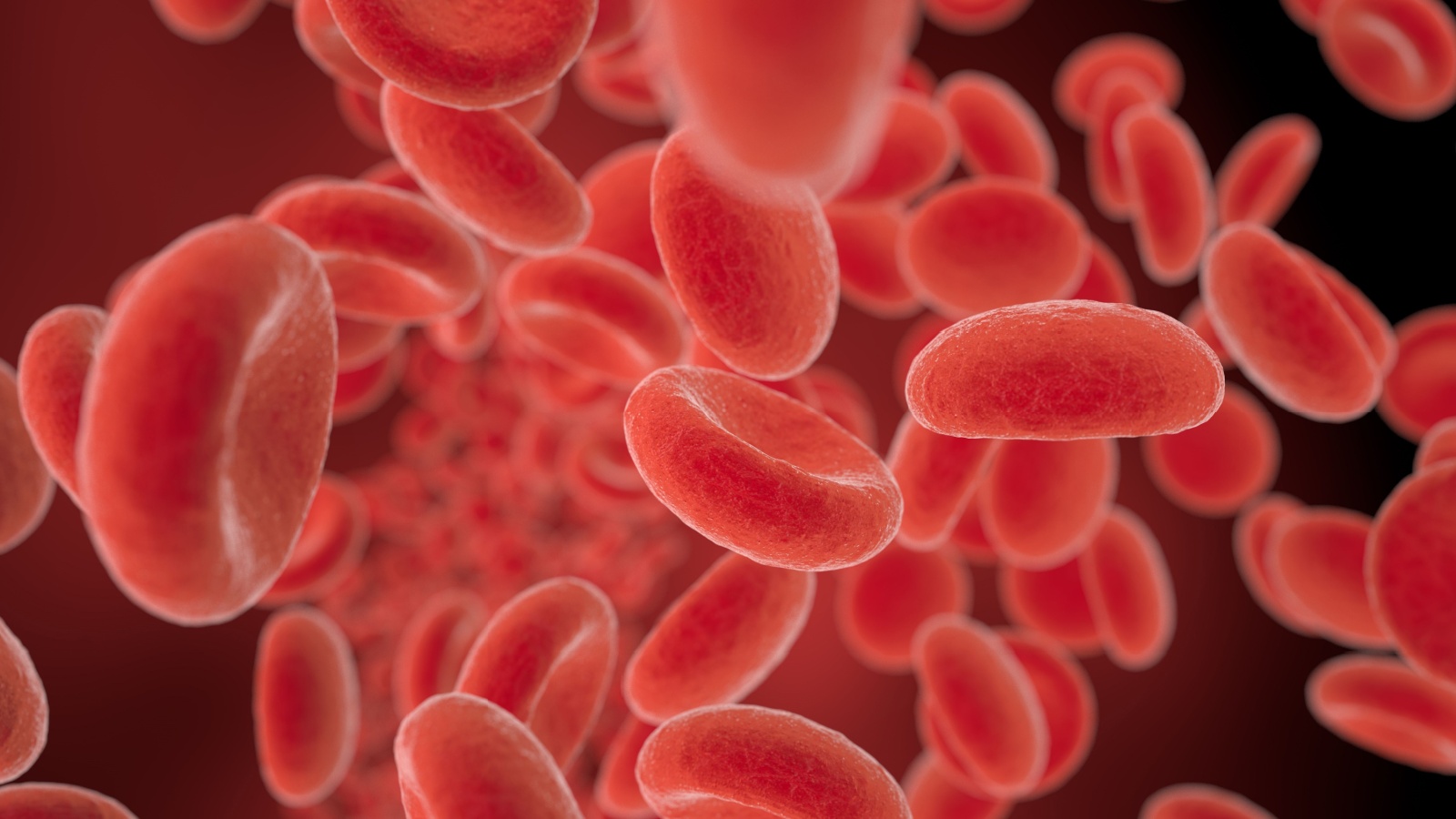
The human circulatory system is incredibly efficient. A single blood cell can travel the entire length of your body in just 60 seconds. Imagine that! In just one minute, that tiny cell has been everywhere from your heart to your toes and back again.
Your heart plays a huge role in this process. It pumps around 70 milliliters of blood with each beat. For the average person, the heart beats about 70 times per minute. This means your heart moves nearly all the blood in your body within a single minute.
There are about 60,000 miles of blood vessels in your body. If you stretched them out, they would circle the earth more than twice! The blood vessels include arteries, veins, and capillaries.
Every type of blood cell—from red and white cells to platelets—uses this network to travel around your body. This keeps you healthy by delivering oxygen and nutrients to your tissues and removing waste products.
Understanding how quickly and efficiently your blood circulates shows just how amazing and complex your body is. Knowing this can inspire you to maintain a healthy lifestyle to keep your heart and blood vessels in good shape. Read more about it here.
Humans Are the Only Animals That Cry Emotional Tears
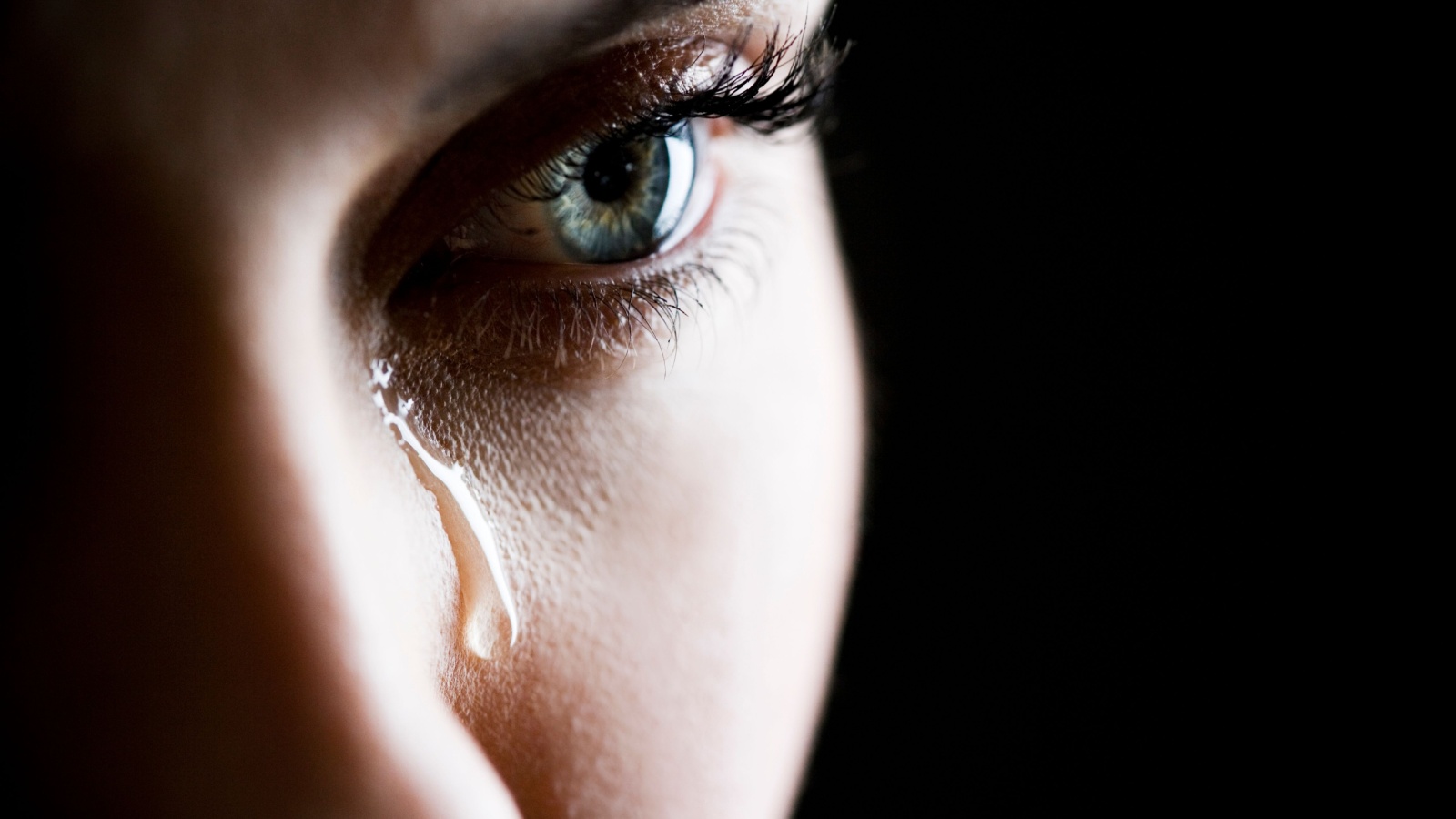

You are unique because humans are the only animals that cry emotional tears. When you watch a sad movie, tears may stream down your face. Other animals don’t cry for emotional reasons like we do.
Scientific research confirms that other species may produce tears, but not due to sadness. For example, some animals shed tears to protect their eyes from irritants. Human tears, though, can be triggered by complex emotions like joy, sadness, or frustration.
Psychologist Randolph Cornelius from Vassar College in New York explains that our emotional tear-shedding is a special human trait. It connects us, showing others we need help or comfort. No other animal shows sadness through crying in this way.
Why exactly humans evolved this ability is still a mystery. Some scientists think it might have something to do with forming social bonds. Emotional tears can signal our need for support from others, strengthening our social connections.
Tears also release stress hormones, giving you a calming effect after a good cry. This means crying can physically help you feel better. While animals may show distress in other ways, human emotional tears are truly unique.
There Are About 100,000 Miles of Blood Vessels in Your Body
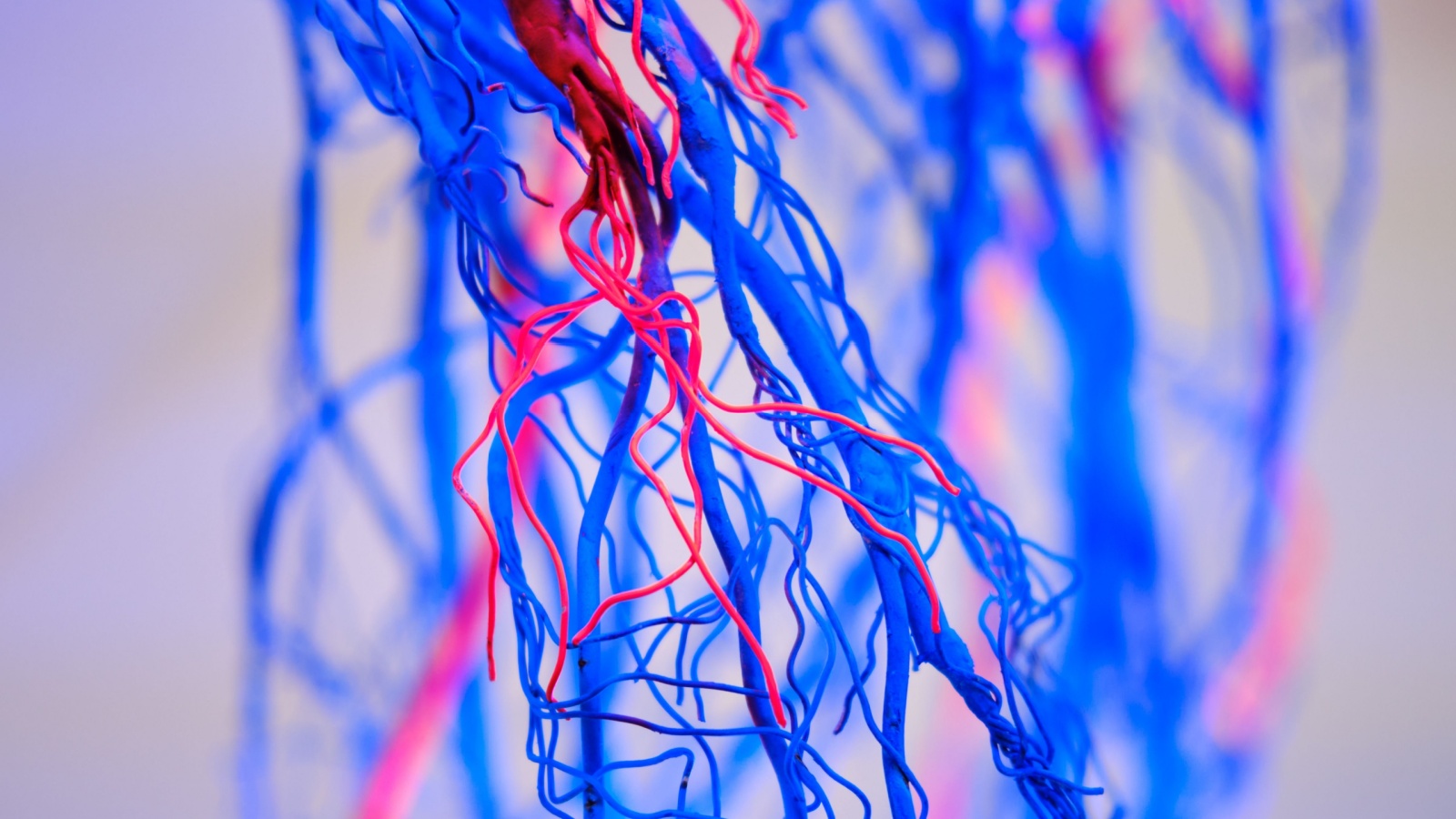

You have roughly 100,000 miles of blood vessels running through your body. This includes arteries, veins, and capillaries. If you laid them end-to-end, they could circle the Earth four times!
Arteries carry oxygen-rich blood from your heart to every part of your body. Veins bring blood back to your heart. Capillaries, the smallest blood vessels, connect arteries and veins.
Your heart keeps this system running by pumping blood through all these vessels. This non-stop journey supplies oxygen and nutrients to tissues and organs, and removes waste products. This process is vital for your survival.
Think about it. Your blood vessels are longer than the distance around the entire globe! This intricate network works tirelessly to keep you alive and healthy. The next time you feel your pulse, remember it’s a tiny part of an enormous system that stretches for thousands of miles.
Understanding this helps you appreciate how complex and amazing the human body truly is. Your very existence depends on this expansive network of vessels working seamlessly within you. You might never see them, but they are there, constantly supporting your life.
Humans Have About 5 Million Hair Follicles
Humans have around 5 million hair follicles on their bodies. This number is similar to our close relatives, like chimps. The difference is in the type of hair that grows from these follicles. Most of the hair on your body is called vellus hair. It’s fine and barely visible.
These tiny hairs cover the majority of your body, except for places like your head, pubic area, and armpits. In these areas, the hair is thicker and more noticeable. The follicles in these places produce terminal hair, which is coarser and darker.
Even though you might not think about it, each hair follicle plays an important role. For example, the hair on your head protects your scalp from the sun. Hair in your nose catches dust and other particles, keeping your lungs clean.
The placement and type of follicles also help regulate your body temperature. In colder weather, the tiny muscles near your follicles can contract, causing your hair to stand up. This traps a layer of air close to your skin and helps keep you warm.
Supernumerary Teeth
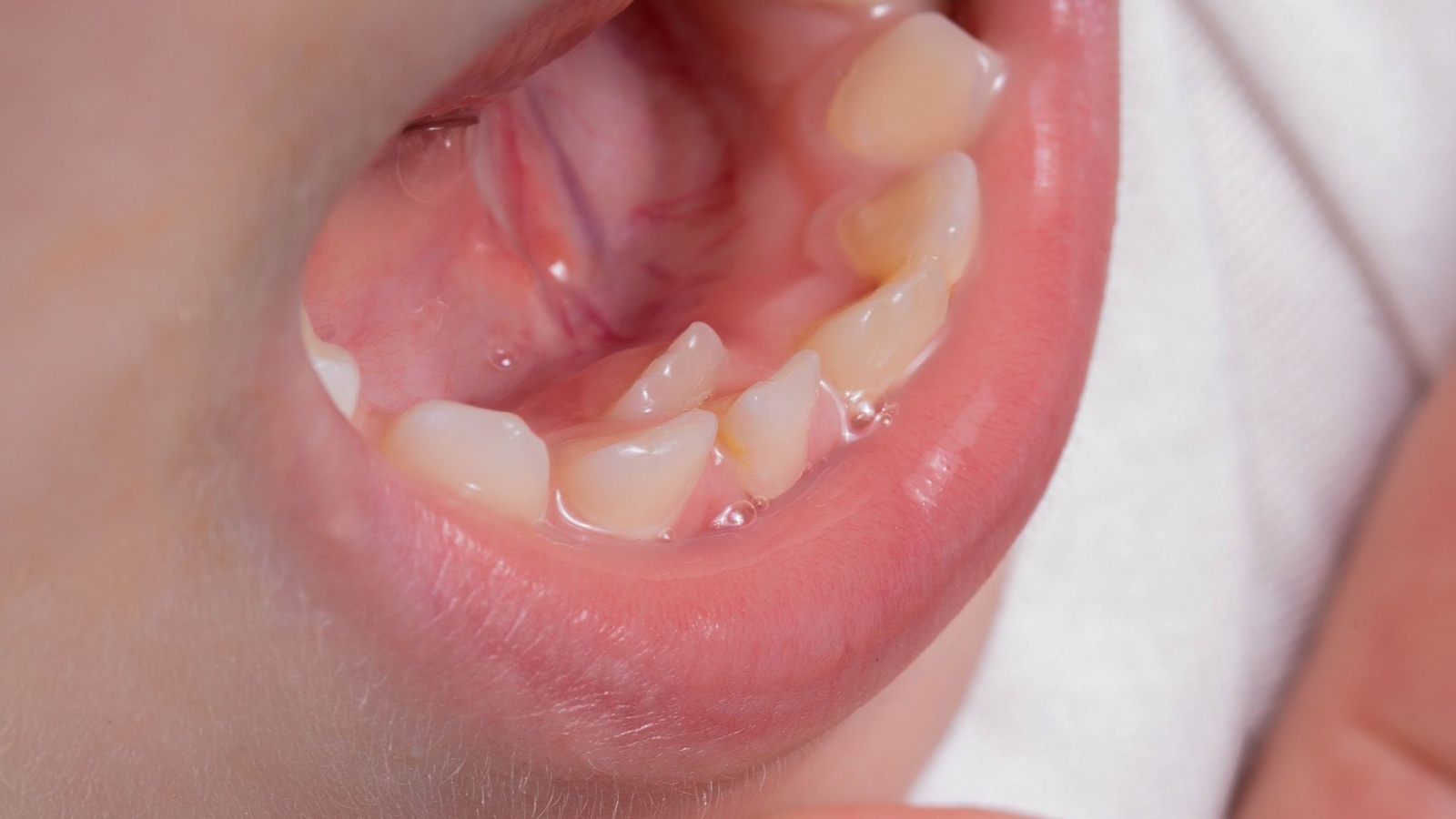
Supernumerary teeth refer to extra teeth that appear in the mouth beyond the usual set of 32 adult teeth. These extra teeth often develop due to genetic factors and can appear anywhere in the dental arch. They’re most commonly found in the upper jaw.
These teeth can cause problems, such as crowding, misalignment, or difficulty in chewing. Sometimes, they might not erupt at all and are only visible on X-rays. Dentists usually recommend removing these teeth to prevent complications.
Common Types of Supernumerary Teeth:
- Mesiodens: Small teeth that appear between the two upper front teeth.
- Distomolars: Extra molars located at the back of the mouth.
Vestigial Structures Like the Appendix
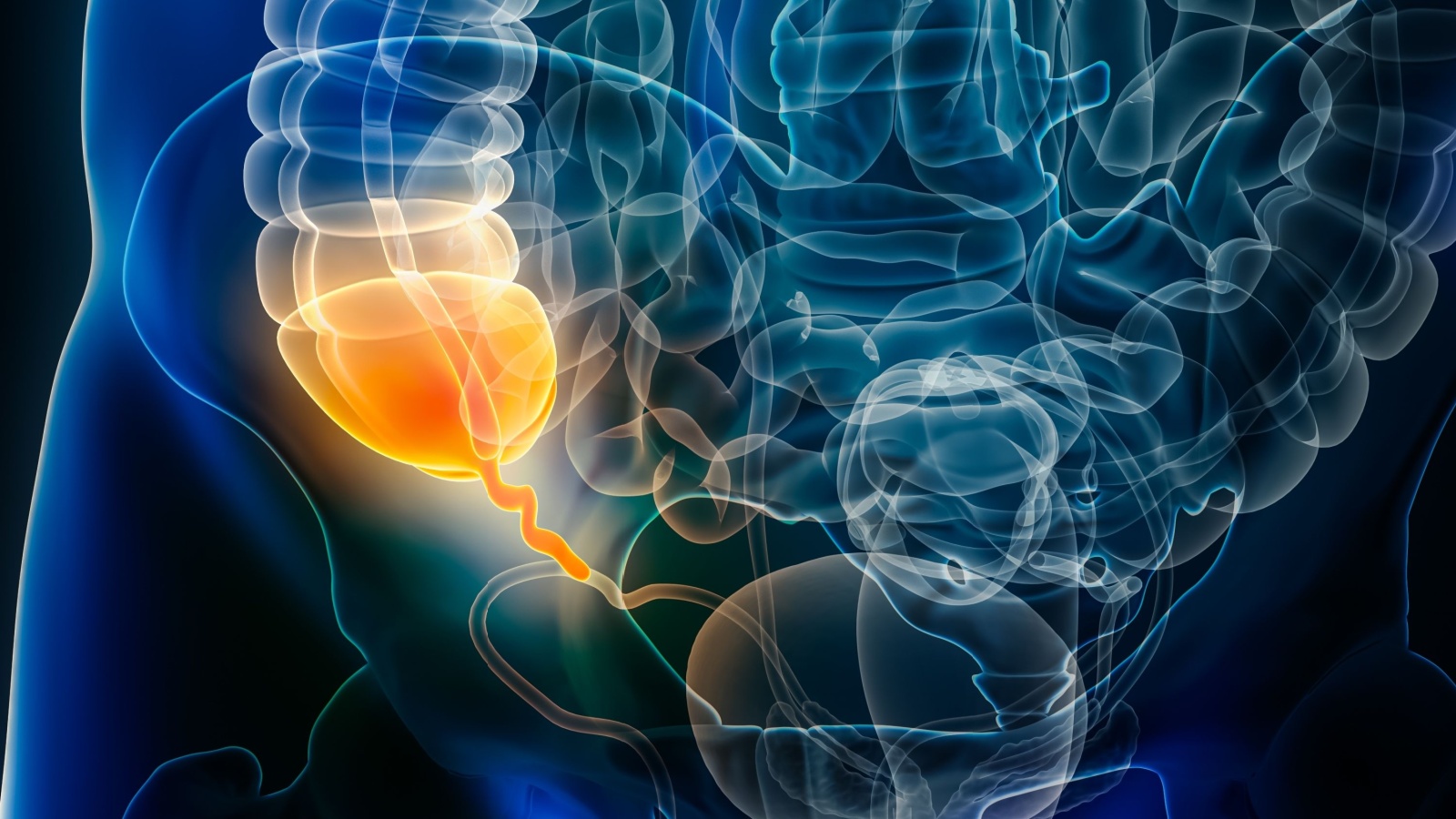
Vestigial structures are parts of the body that have lost their original function through evolution. The appendix is one of the most well-known vestigial organs. It’s a small tube connected to the large intestine.
Although it doesn’t serve a vital role in modern humans, it might have helped our ancestors digest cellulose from plants. Today, the appendix can become inflamed, leading to appendicitis, a condition that often requires surgical removal.
Other Examples of Vestigial Structures:
- Coccyx (tailbone): A remnant of a tail our ancestors might have had.
- Wisdom Teeth: Extra molars that were useful for our ancestors’ rough diet.
These anatomical anomalies are fascinating glimpses into both the diversity and history of the human body.
Photic Sneeze Reflex
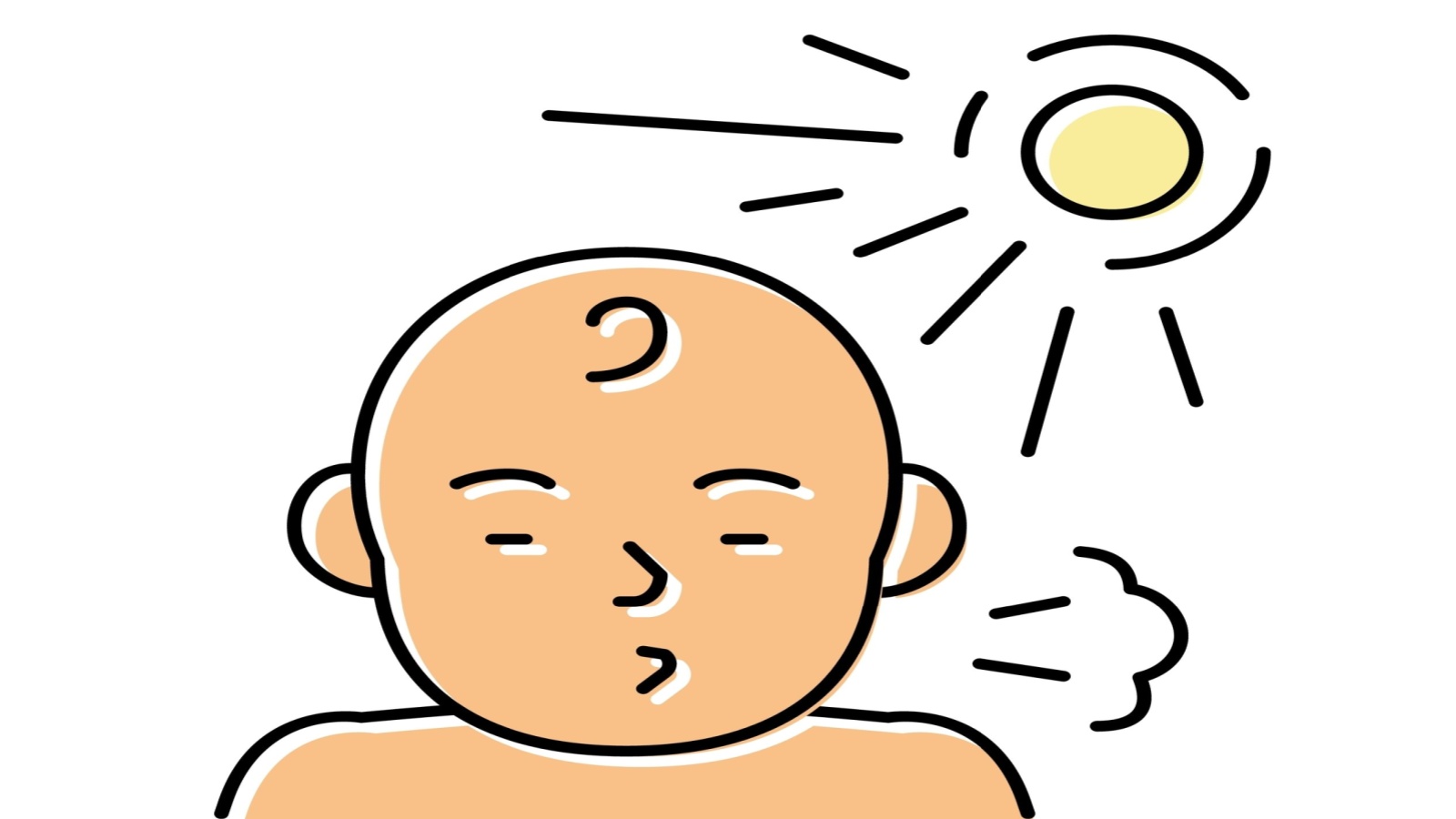
Have you ever sneezed when you looked at the sun or a bright light? This is known as the photic sneeze reflex. About 18-35% of people experience this reflex, which is believed to be genetic. Scientists think it may occur due to a crossing of signals in the brain. When bright light stimulates the optic nerve, this may also trigger the trigeminal nerve, causing a sneeze.
This reflex can be a bother in certain situations, like driving. It usually triggers when transitioning from a dark to a bright environment. Interestingly, the exact biological reason behind this reflex isn’t fully understood, making it a fascinating area for future research.
Pilomotor Reflex

Another curious reaction is the pilomotor reflex, more commonly known as goosebumps. This occurs when tiny muscles at the base of hair follicles contract, causing hair to stand on end. You may get goosebumps when you’re cold, scared, or even emotionally moved by music or memories.
This reflex is a leftover from our ancestors, who had more body hair. For them, raising hair would trap air and provide warmth or make them appear larger to predators. Today, it serves little practical purpose but is a clear demonstration of the body’s automatic response mechanisms.
Both these reflexes are small reminders of the complex and often mysterious ways our bodies work.
Katy Willis is a writer, master herbalist, master gardener, and certified canine nutritionist who has been writing since 2002. She’s finds joy in learning new and interesting things, and finds history, science, and nature endlessly fascinating.