The platypus, one of the most unusual creatures on Earth, possesses a venom that has baffled scientists for years. This venom, produced by males during the breeding season, contains many unique properties that defy explanation. Here are 14 astounding facts about platypus venom that continue to intrigue researchers.
Only Males Produce Venom
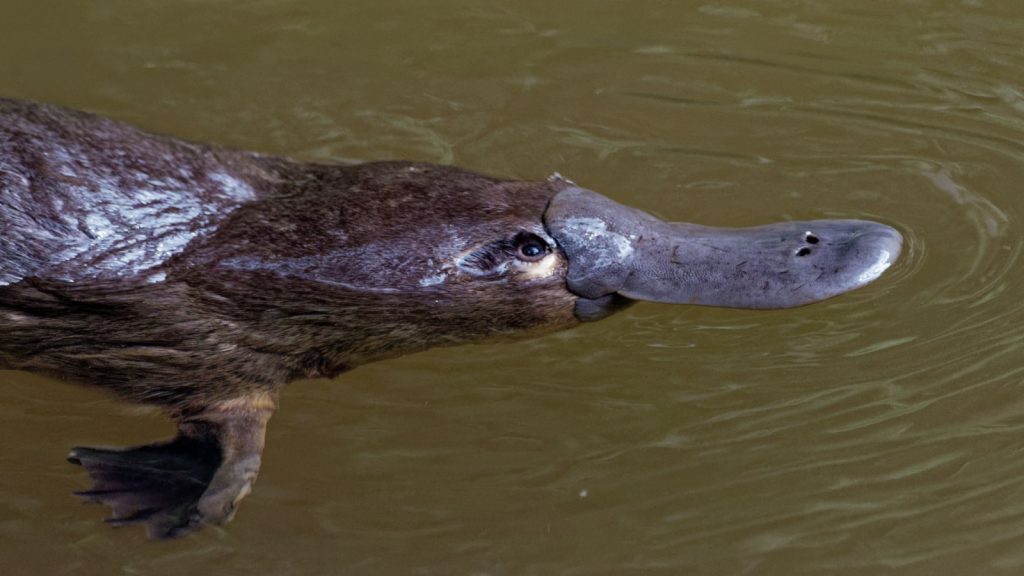

Male platypuses have venomous spurs on their hind legs, which they use during mating season to compete with other males. Females have spurs as well, but they do not produce venom.
Seasonal Venom Production

The venom is only produced during the breeding season, suggesting it plays a role in competition among males. Outside of this period, the venom glands shrink, and venom production ceases.
Complex Venom Composition

Platypus venom contains over 80 different toxins, many of which are unique to this species. These toxins include defensins, which are proteins also found in the immune system, but their exact function in venom remains unclear.
Painful But Not Fatal to Humans

While platypus venom is not deadly to humans, it causes excruciating pain that can last for weeks or even months. The pain is resistant to conventional painkillers, adding to the mystery of its effects.
Unique Protein Structures

Some proteins in platypus venom have unusual structures not found in other venomous animals. These unique structures suggest the venom evolved independently, making it a subject of interest in evolutionary biology.
Potential Medical Applications

Researchers are studying platypus venom for potential medical applications, such as pain management and antimicrobial treatments. The unique properties of the venom could lead to new breakthroughs in medicine.
Inflammation and Swelling

In addition to causing pain, platypus venom induces significant inflammation and swelling at the site of the sting. The mechanisms behind these effects are still not fully understood.
Evolutionary Enigma

The evolutionary origins of platypus venom are puzzling. It shares some similarities with reptile venom but appears to have developed independently, highlighting the platypus’s unique place in the animal kingdom.
Targeted Towards Mammals

The venom seems to be specifically effective against other mammals, which aligns with its use in male competition. Its effects on different types of animals vary significantly.
Resistance to Antivenom
Currently, there is no known antivenom for platypus venom. This resistance to treatment makes it a unique and challenging subject for medical research.
Impact on Victim’s Mobility

The venom can cause temporary paralysis or severe muscle weakness in the affected area. This effect helps males incapacitate rivals during fights.
High Energy Cost
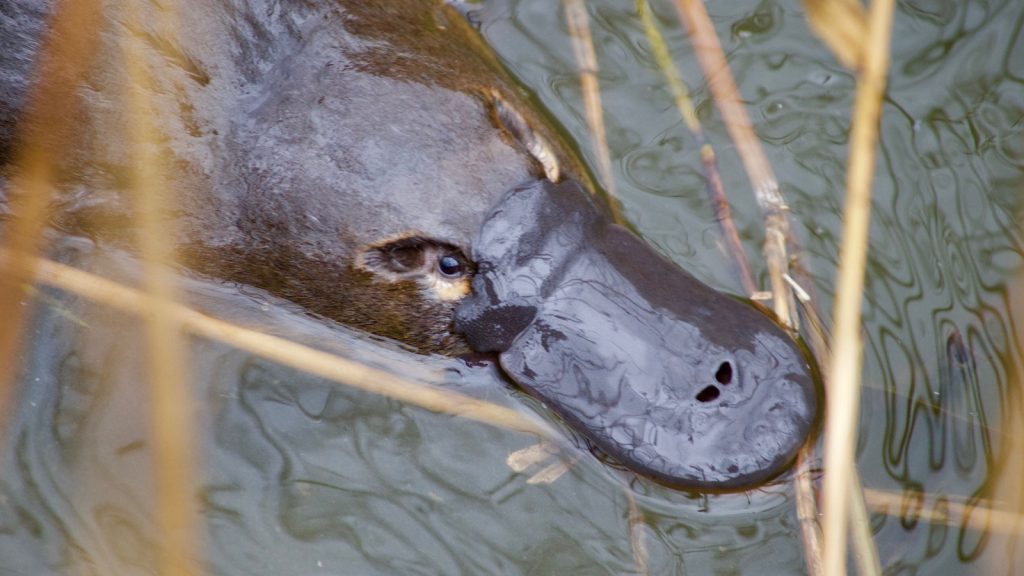

Producing venom is energetically costly for male platypuses. This high energy cost suggests the venom’s importance in their reproductive strategy, but the exact benefits remain speculative.
Rare in Nature

Venomous mammals are extremely rare, making the platypus an outlier. This rarity adds to the intrigue and scientific interest surrounding their venom.
No Observable Effects on Other Platypuses

Interestingly, platypus venom does not seem to have a significant impact on other platypuses, indicating a level of immunity within the species. This immunity is yet another aspect that scientists do not fully understand.
Platypus venom remains one of nature’s most intriguing mysteries. Each discovery about its composition and effects opens new questions, keeping scientists fascinated and eager to learn more.
Ellen has been obsessed with logic puzzles, jigsaws, and cryptograms since she was a kid. After learning she was taught how to play chess wrong by a family friend (so they could win), she joined her school chess club and the rest is history.


